Write an Ansible PlayBook that does the following operations in the managed nodes -
🔹 Configure Docker package
🔹 Start and enable Docker services
🔹 Pull the apache httpd server image from the Docker Hub
🔹 Run the apache httpd container and expose it to the public
🔹 Copy the HTML code in /var/www/html directory and start the webserver
prerequisites -
Configure Ansible on the controller node.
Controller Node and managed nodes should have network connectivity.
So, let's get started
Configure Controller node inventory file. Add all the hosts managed nodes in it.
[docker]
192.168.43.39 ansible_ssh_user=root ansible_ssh_pass="<password of node>"
here, I am adding only one node. but we can add as many as we want to configure a web server
Ansible Playbook
Write Ansible Playbook for configuring docker for Apache Web server.
so, create a workspace in the controller node. start writing ansible-playbook and extension should be .yml or .yaml of the file because we write playbook in YAML language.
- name: "Configure Docker"
hosts: docker
gather_facts: yes
vars:
- image: "httpd"
- webpages: "index.html"
- webpath: "/root/web/"
tasks:
- name: "Check Docker package Installed or Not"
shell: "rpm -q docker-ce"
register: checkd
ignore_errors: yes
- name: "Debug check docker package"
debug:
var: checkd
here, I added my hosts (managed nodes) as ‘docker’ as I write in the inventory file. and created some variables which we gonna use later in the playbook.
First I have checked whether the docker package is already installed or not on the managed node. If the ‘docker’ package is not installed then it will give us an error and that error we can use further as a condition in the playbook which we will see ahead in the playbook.
Configure yum repository and Install docker-ce package
If the above code gives an error then this code will run and configure the yum repository to Install the docker-ce package. And if the docker-ce package is already installed on the managed node then these both steps will be skipped.
- name: "configure yum for docker-ce"
yum_repository:
name: Docker
description: Repository for Installing Docker-ce package
file: docker
baseurl: https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/
gpgcheck: no
when: ( checkd.failed == true or checkd.rc != 0 )
register: yum
ignore_errors: yes
- name: "Debug yum configuration"
debug:
var: yum
- name: "Install docker-ce package"
shell: "{{ ansible_pkg_mgr }} install docker-ce --nobest -y"
when: ( checkd.rc != 0 or checkd.failed == true ) and ( yum.state == "present" )
register: installdocker
- name: "Debug Install Docker"
debug:
var: installdocker
Here, I have used the shell module of ansible because the yum or dnf module does not have any nobest option, This is one of the limitations of Ansible.
Installation of
docker-cepackage depends on two conditions -
when there is no
docker-cepackage is already installed on the managed node.And when the
yumrepository is created successfully.
Start and enable Docker services
- name: "start Docker services"
service:
name: docker
state: started
enabled: yes
register: srvc
- name: "Debug Docker Service"
debug:
var: srvc.changed
From this block of code, the docker service will start and enable on the managed nodes.
Install
dockerpython library
For pulling any docker image from hub.docker.com or doing anything on the docker container we need the docker or docker-py library on the managed node. otherwise, any of docker-related ansible modules will not work on the managed node.
- name: "Check Docker python Library is Installed or Not"
shell: "pip3 list | grep docker"
register: dockerLibrary
ignore_errors: yes
- name: "Debug docker Library"
debug:
var: dockerLibrary
- name: "Install python36 package"
package:
name: python36
state: present
register: ipython
when: dockerLibrary.rc != 0 or dockerLibrary.failed == true
- name: "Debug python36 package"
debug:
var: ipython
- name: "Install docker library"
pip:
name: "docker"
when: ( dockerLibrary.rc != 0 or dockerLibrary.failed == true ) and ipython.rc == 0
Like before I checked the docker package, and if it is not installed then I write yum module and package module, likewise here also first I checked for the docker python library, and if it is not installed then first it installs python36 package and then it will install docker library.
Pull
httpd(Apache) Docker Image
- name: "Pull Docker Images"
docker_image:
name: "{{ image }}"
source: pull
the variable we created at the top of the playbook ‘image’ we have used here. and this code will pull httpd image from Docker HTTPD Image . this is why all our managed nodes should have Internet connectivity.
Copy Web Pages
create a new file in your workspace. name it anything and give extension .html. I named my file index.html
<h1>Welcome!!! to my Web Server</h1>
<h2>Hello This is Shashi Kant</h2>
<h3>This is Docker Container from Ansible</h3>
I write these three lines for testing.
- name: "Create Directory to copy web pages"
file:
path: "{{ webpath }}"
state: directory
register: mkdir
- name: "Debug create Directory"
debug:
var: mkdir
- name: "Copy Web Pages"
template:
src: "{{ webpages }}"
dest: "{{ webpath }}"
register: copywebpages
- name: "Debug Copy web pages"
debug:
var: copywebpages
Now add this code in the playbook for copying web pages. And finally, launch Docker Container.
Launch Docker Container
Now finally write code for launching the docker container. and expose it to the public world. as they also can access your website.
- name: "Launch Docker Container"
docker_container:
name: ansibleWebContainer
image: "{{ image }}"
state: started
exposed_ports: "80"
ports: "8080:80"
volumes: "{{ webpath }}:/usr/local/apache2/htdocs/"
network_mode: bridge
restart: yes
restart_policy: always
when: mkdir.failed == false and copywebpages.failed == false
using the docker_container module we can launch the docker container. here I used httpd Images. and expose it to the public world on port no. 8080. and it is using volume of the managed node where we have copied our web pages.
Used bridge type network as network_mode in the container, it will provide network connectivity in a docker container.
I used restart and restart_policy here because it will give me some little management of the container. like if my container goes down due to some reason then docker will automatically launch the same new container for me, with same web pages. until I manually delete or stop this container.
And this play runs only when our above code of copying web pages and creating directory will run successfully.
Now, Finally, Run Ansible Playbook.
ansible-playbook <name_of_ansible_playbook.yml>
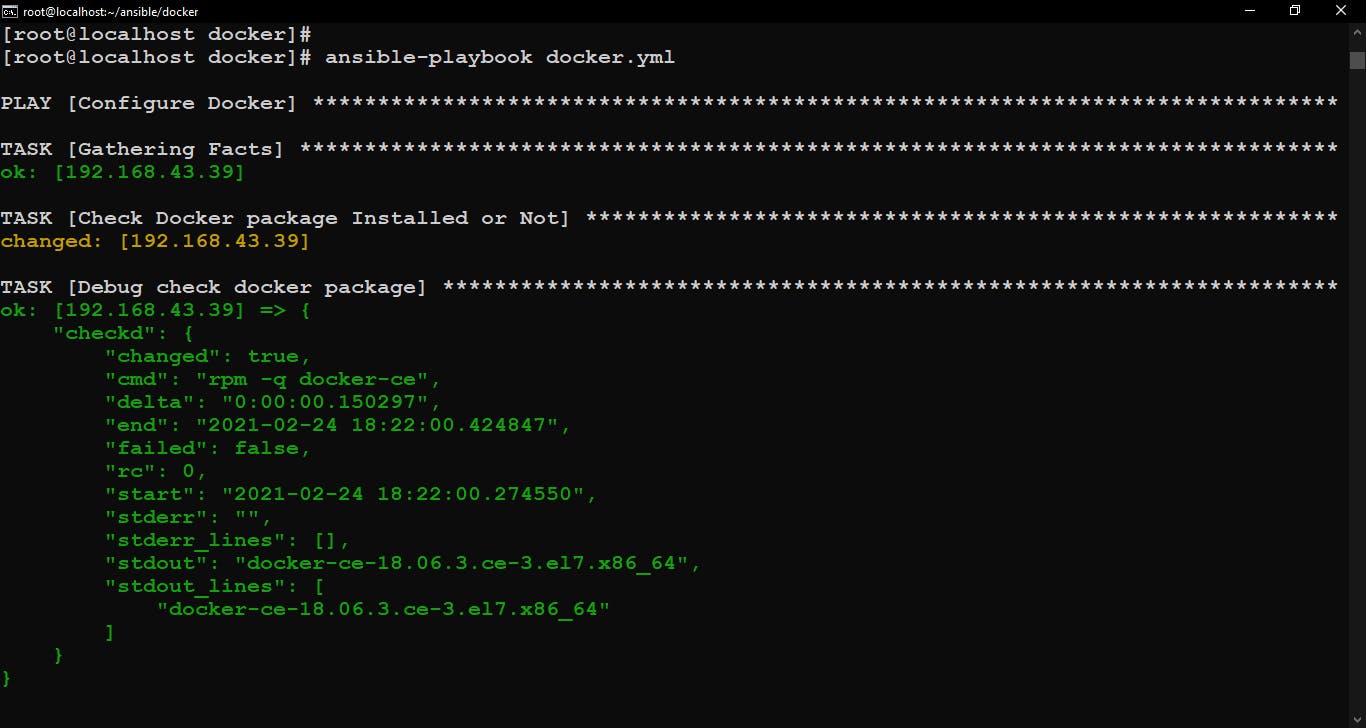
Run Ansible Playbook
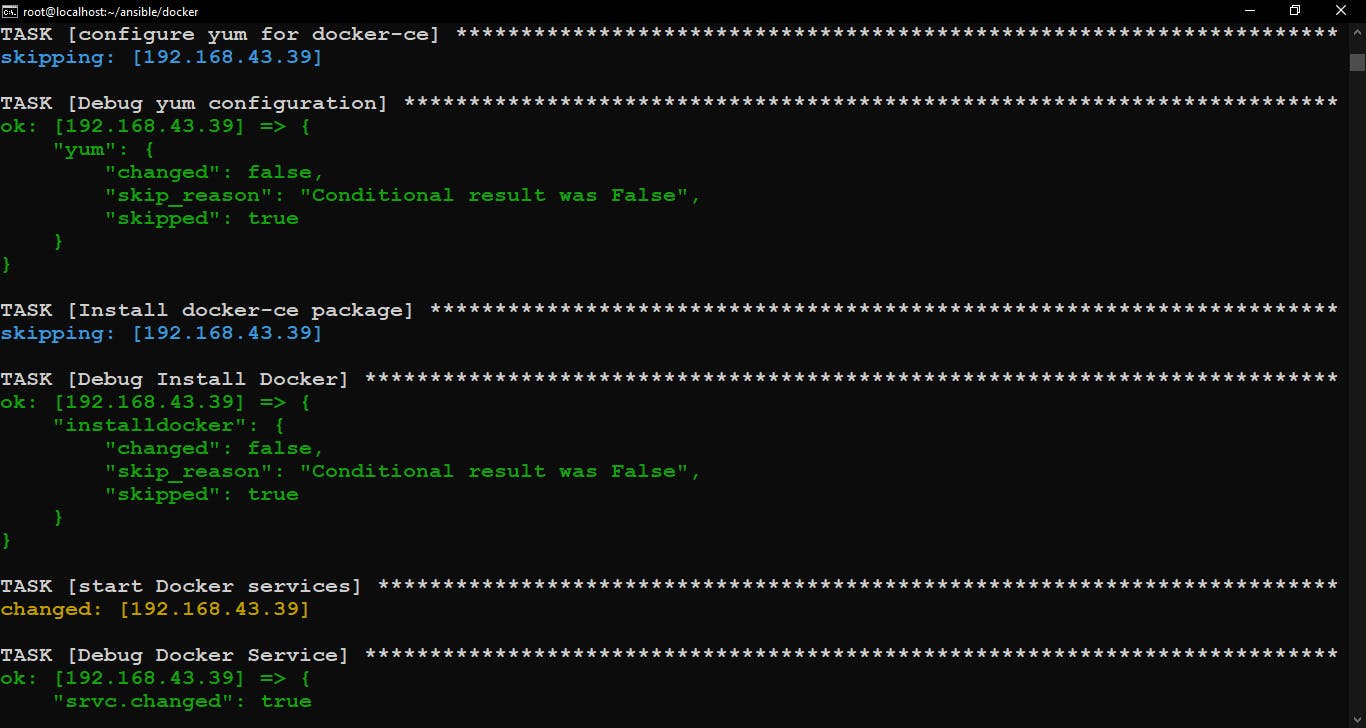
Configure yum and Install docker-ce package if not Installed and skip these plays if already configured and Installed
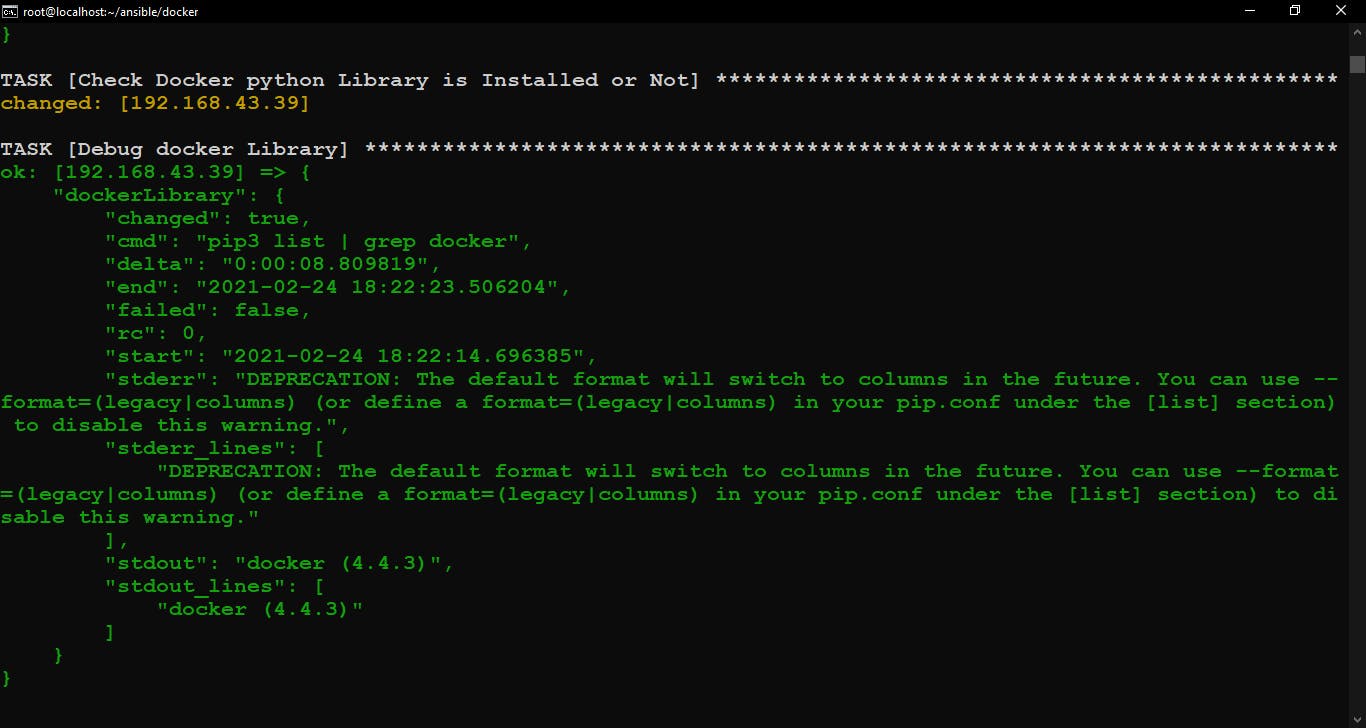
Check docker library is installed or not.
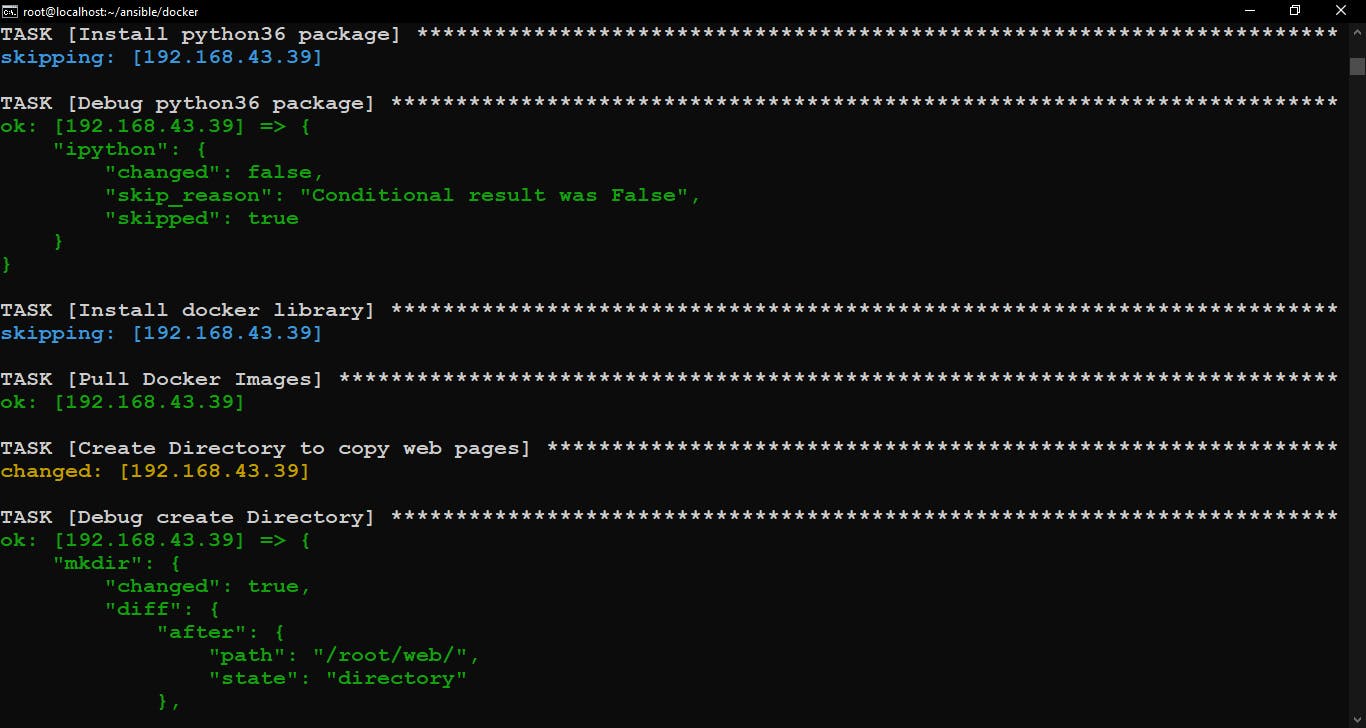
If the docker library is not Installed then Install the python36 package and Install the docker library otherwise skip these plays. And Create a directory to store web pages.
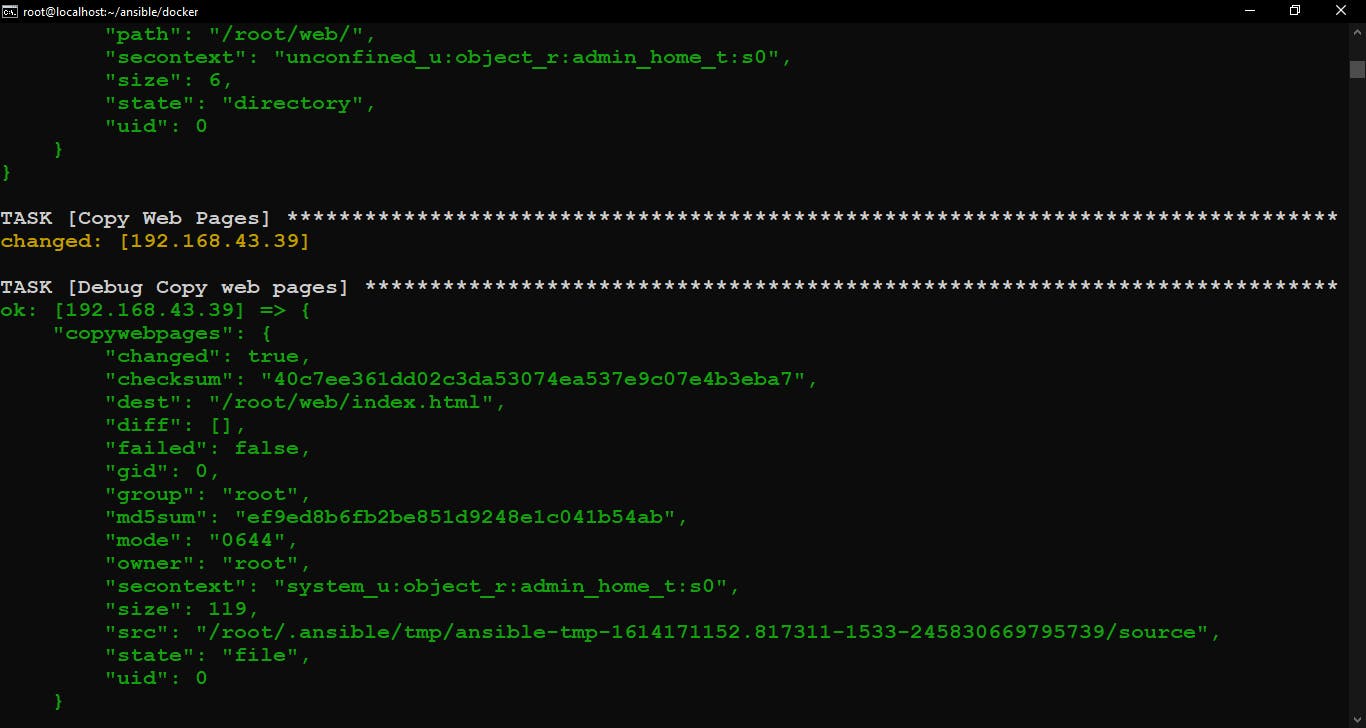
Copy web pages to the managed node.
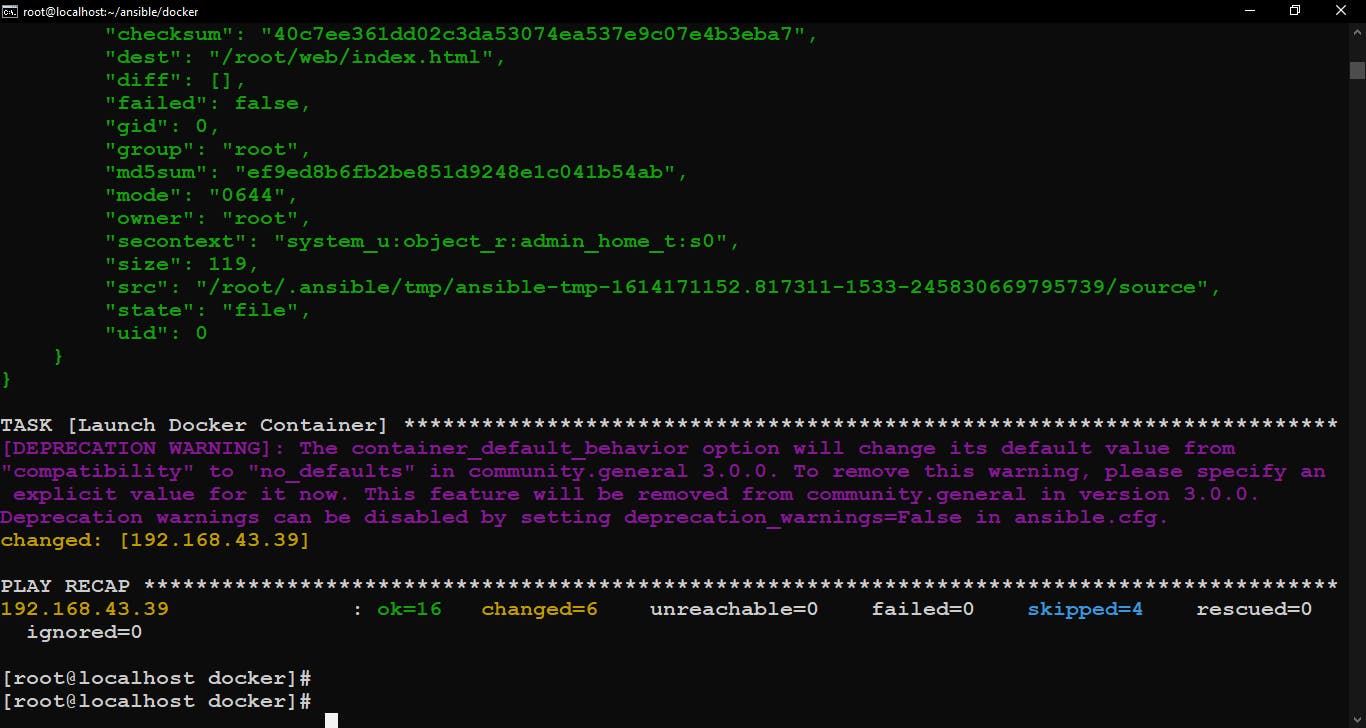
Finally, Launch the Web Server on Docker Container.
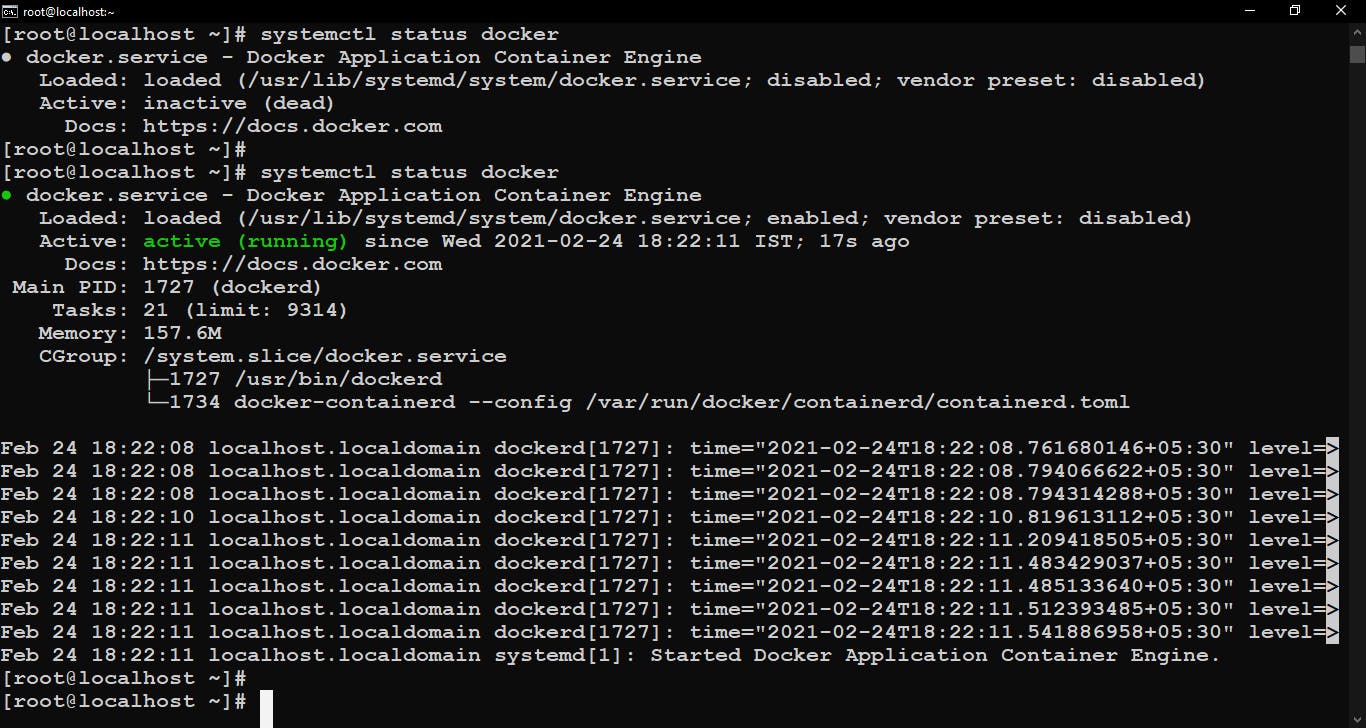
Checking Docker services before and after running the playbook.
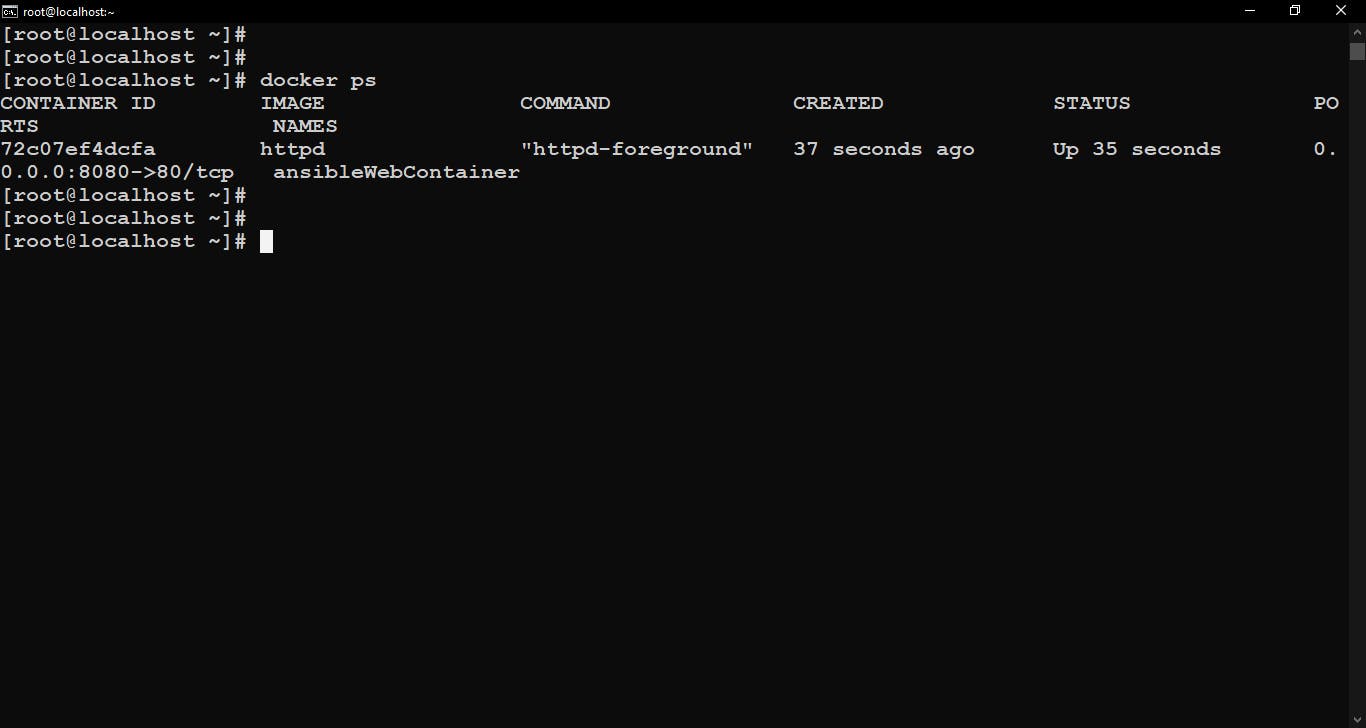
docker ps command to see the active docker containers…here we can see this container is launched by Ansible with httpd image and expose to port no. 8080.
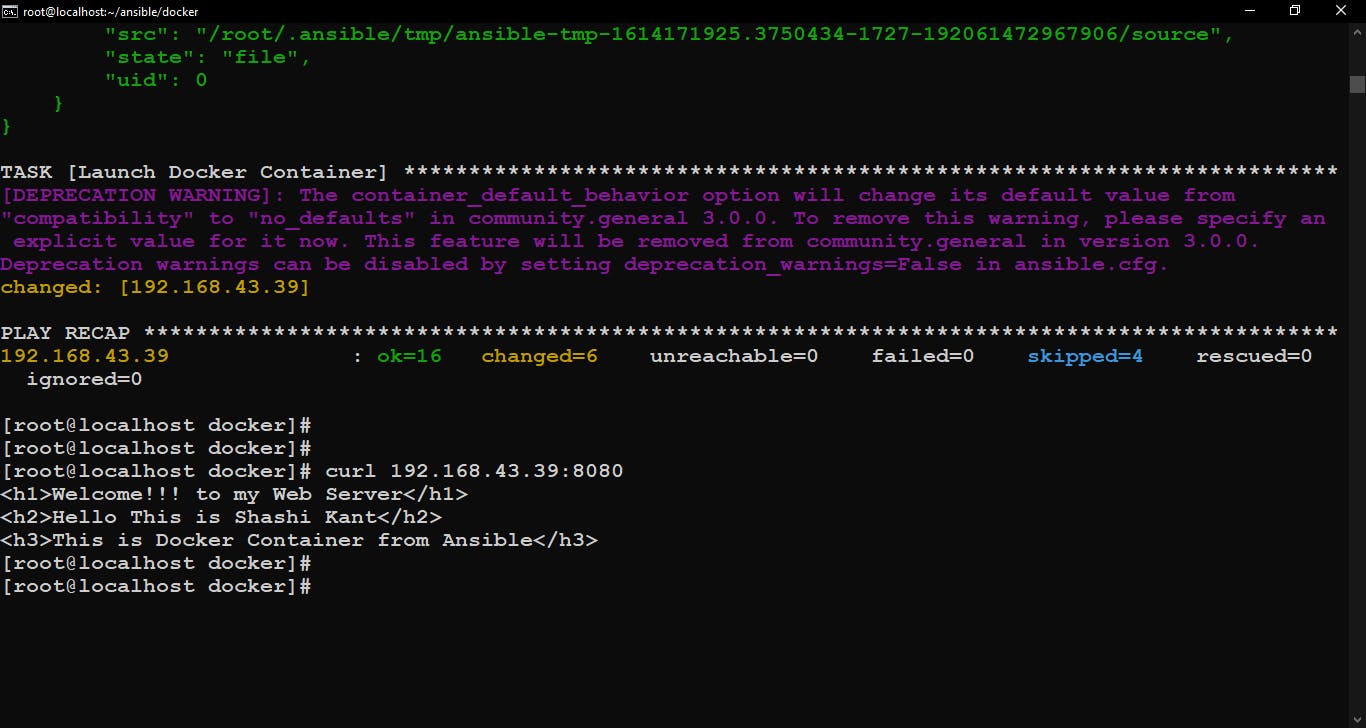
We can check our web server by using the curl command
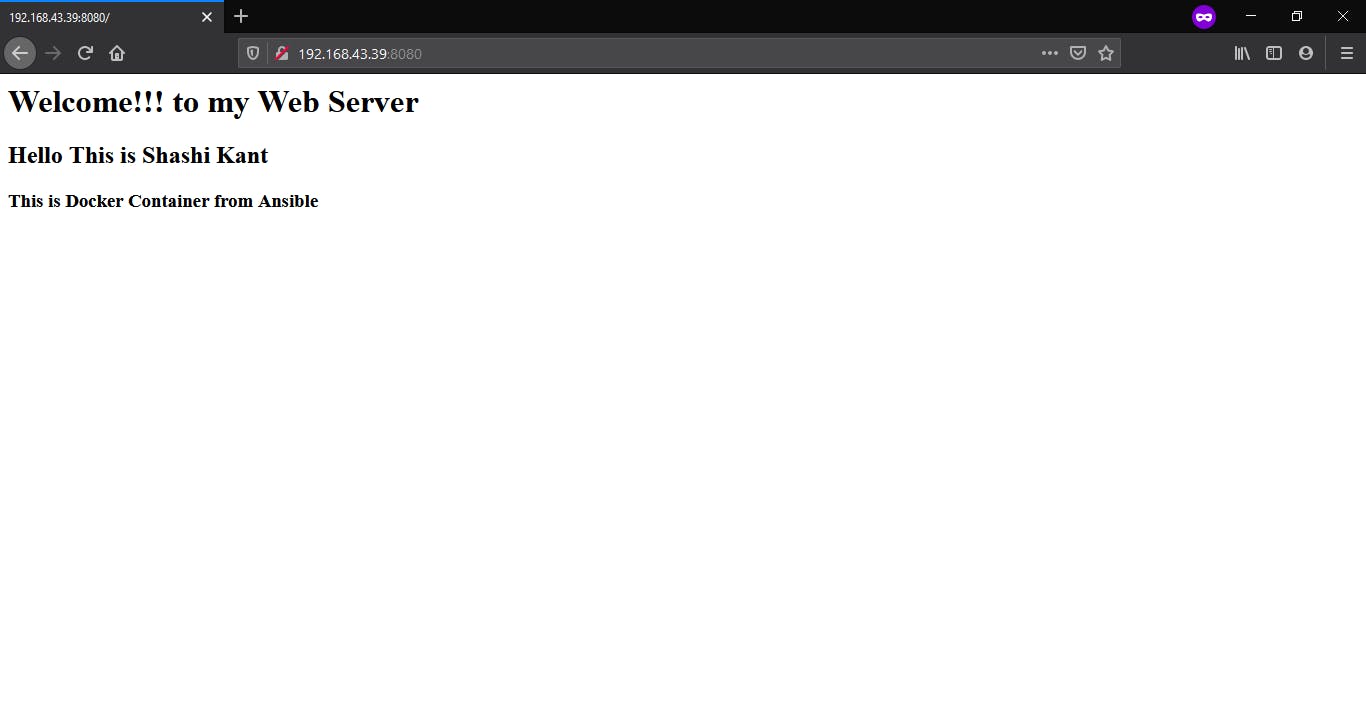
Or, we can check our web server on a web browser.
GitHub Repository Link for my Ansible code - GitHub Repo
That’s All, Keep Learning.
! THANK YOU For Reading !